
The revised Payment Services Directive, commonly known as PSD2, came in January 2018 and since then has been changing the financial services industry across the countries of the European Union prominently.
The principal goals of PTS2 are improvement of consumer protection, reinforcement of security in the payments market, encouragement of competition, and facilitation of innovation in the financial service sector. Exclusively, PSD2 aims to boost competitiveness and innovations by bringing new players, Third-Party Providers, also referred to as TTPs, into the payment value chain.
Specifically, this directive grants these new players equal opportunities to access financial data provided by banks and allows them to bring technological expertise and offer their ideas and solutions to the market.
These new players in financial services can be of three distinct types that correspond to the three new services permitted by the revised PSD. These three types of TTPs are shortly discussed below.
Card Issuers Service Providers, also known as CISPs, are authorized third-party companies that, unlike banks, do not directly hold funds but can still issue debit cards linked to accounts held at other financial institutions.
Payment Initiation Service Providers, better known as PISPs, are third parties that are licensed to make a payment transaction on behalf of customers. As PISPs contain all bank details, they allow consumers to initiate payments directly from their bank account instead of using a credit or debit card.
Account Information Service Providers, commonly called AISPs, are third parties that are accredited to access a consumer‘s account data held by financial institutions to share it with other third parties with the explicit consent of the customer.
As account information services are the most demanded concerning the banking industry, it is appropriate to deeper understand how third parties that provide these services work.
What exactly does an AISP do?
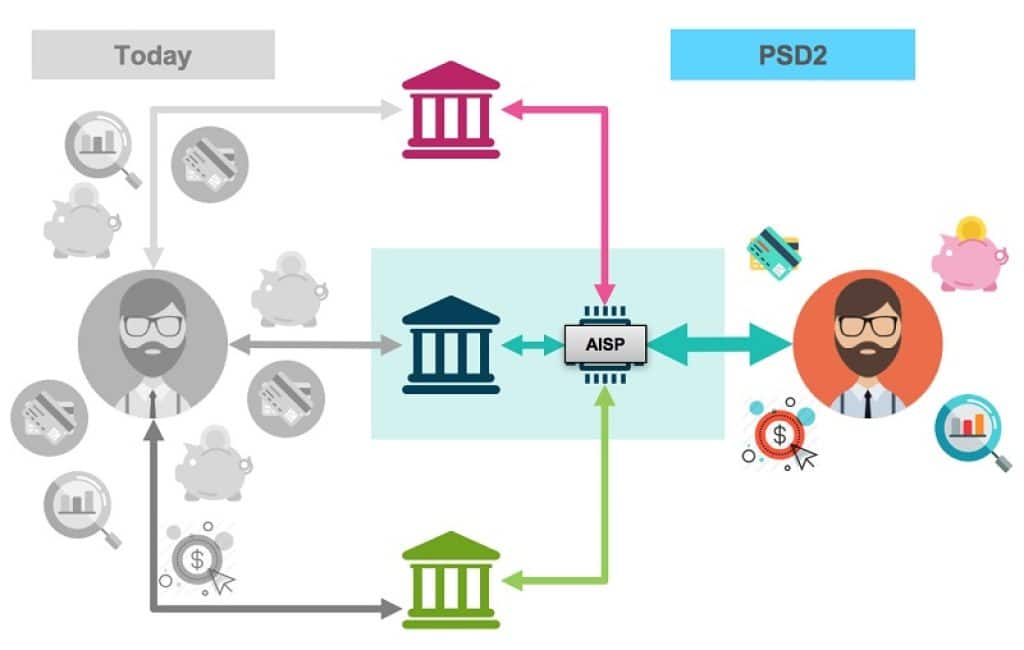
As already mentioned, an AISP is a licensed company that can legally access an account holders‘ information and, in turn, transfer this information back to customers or other third-party providers at the request of the user. AISPs usually are fintech companies, banks, or other companies providing financial services.
When licensed as AISPs, companies can retrieve any financial information, including the name and number of the account, balance, standing orders, direct debits, transactions, etc. By accessing data, these account information services suppliers also can store and consolidate information from all customer payment accounts held on multiple payment service providers.
In turn, AISPs can deliver a consolidated view of the consumer‘s financial situation. Also, AISPs can use gathered data exclusively for analysis, aggregation, advisory and informational purposes. In addition, AISPs can only access, store and transfer consumers‘ account information and cannot take any other actions regarding account data, such as instigation of payments or transfers.
Most importantly, companies that provide account information services can only receive account data if consumers themselves, not the account-holding financial institution, provide explicit consent.
How AISPs access data?
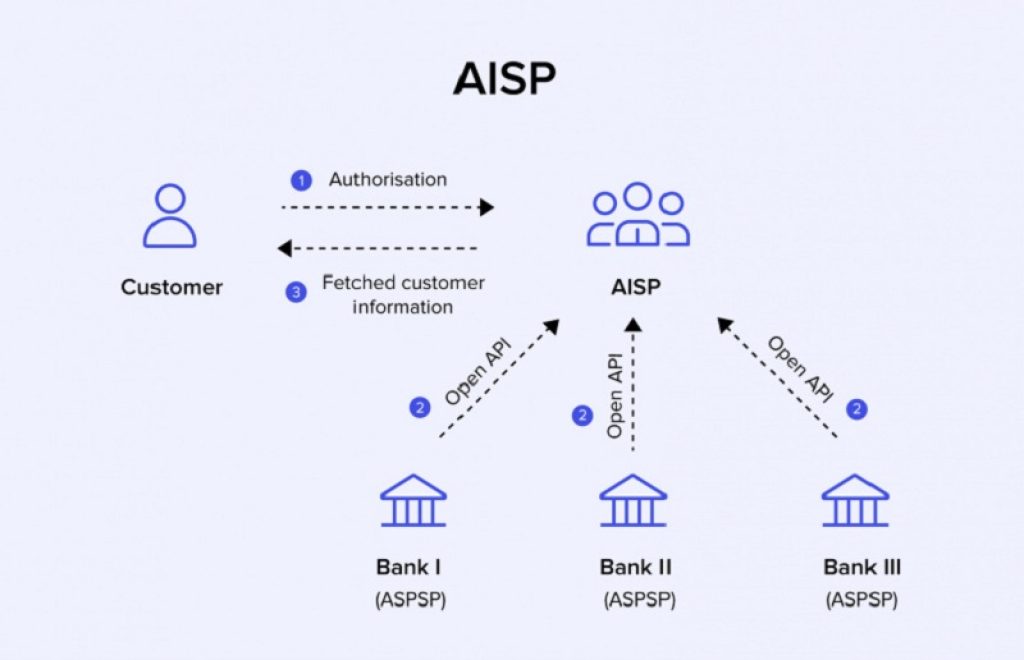
Technically, AISPs access information stored with account-holding financial institutions, and customers reach their accounts through third parties thanks to the usage of APIs, also known as Application Programming Interfaces.
APIs, as special software, allows a convenient and easy way of the interchange of information across financial institutions and AISPs and time-efficient delivery of this data to their consumers. Also, from a regulative perspective, PDS2 strictly governs the utilization of these AIPs and the exchange of data between different parties.
Firstly, PSD2 requires banks to share data with third parties through open APIs transparently and securely. Also, this directive determines that AISPs can not access and collect personal and financial data of consumers for purposes other than for providing the account information services requested by users.
In addition, to become an AISP and get access to consumers‘ financial information, companies must go through rigorous application processes and obtain an AISP license. The rules for the interchange of data and deployment of APIs ensure simplified procedures with maximum security and more choice available and therefore provide a better consumer experience.
How AISPs benefit consumers?

AISPs benefit consumers in numerous ways. Firstly, thanks to account information services, many previous paper-based transactions and application processes have become digitized and, in turn, save customers from exhausting and time-consuming paperwork.
Also, as already mentioned, AISPs store financial information from multiple accounts and present it in one dashboard, allowing customers to evaluate their financial situation, create a budget, and keep track of their spending.
By granting permission for AISPs to access their account, consumers can conveniently and time efficiently get the services they need the most. Thanks to AISPs, consumers can get the best financial advice on how to use their funds, speed up applications for a loan, credit, or other financial services, and acquire more tailored financial suggestions.
To sum up, AISPs provide customers with a complete and understandable overview of their account information that allows them to make the most of their financial data.










