
Electrical connectors are designed to connect two or more electrical devices. They can be used in a variety of ways, from joining entire electrical systems within buildings and vehicles, all the way to connecting individual components and wires.
Electrical connectors come in a wide array of shapes and sizes and serve many different functions. The specific way that they accomplish this task is what sets them apart from each other. Determining the correct type of connector for your application requires an understanding of how it will be used and under what circumstances.
This article will familiarize you with the basics of the different types of connectors and explain what they are used for.
Industrial Power Connectors
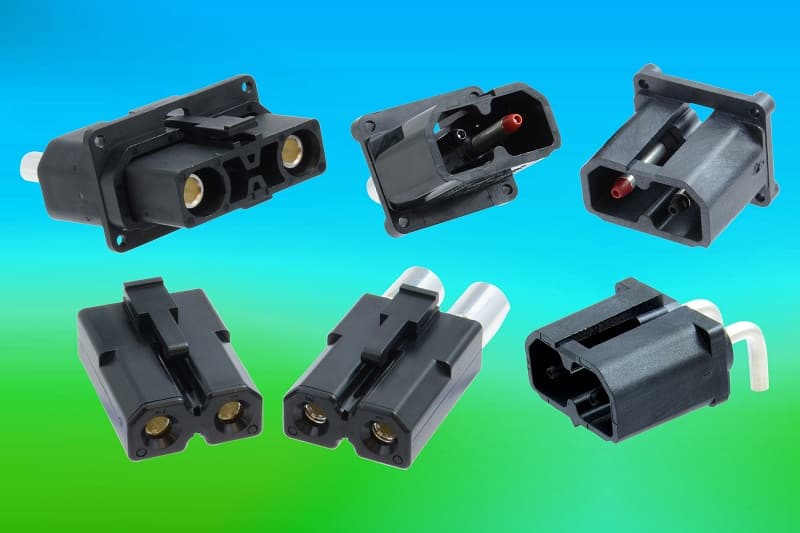

Electrical connectors used in industrial applications are subjected to extreme wear and tear, making them some of the most durable types of connectors. No matter how much vibration or movement is involved during operation, the connector must remain faultless, otherwise, it could lead to costly downtime, equipment failure, or even personal injury.
On top of this, environmental factors such as moisture have harsh effects on electrical connections that are present inside machines that are being operated outdoors. Generator and powersafe connectors are typically used in these types of applications. A powersafe connector is designed to disconnect with very little effort, while generator connectors require the use of a special tool to disconnect.
These connectors are ideal for use in hazardous conditions because they make it easy to isolate components that may pose a threat, such as turning off unneeded pumps or power supplies during an emergency.
Magnetic Connectors
Magnetic connectors consist of two separate metal pins that create an electric circuit when brought into close contact with each other because magnets attached to either end attract them to one another.
These types of connectors are commonly found on microphones and headphones, where they serve as a means of connecting audio signals from various instruments or sound sources before ending up at the output device (i.e., speakers or recording equipment).
For example, a microphone might be connected to a mixer using a magnetic connector, and the output from the mixer would be connected to speakers using another magnetic connector.
This way, electricity flows in one direction between each step in the chain but cannot flow backward because magnets only attract objects that are ferromagnetic (i.e., contain iron), and earbuds and other devices do not contain enough iron to be attracted by the same magnet which powers an electric guitar amplifier.
Twist Lock Connectors
Twist lock connectors receive their name from the locking mechanism that enables them to maintain a tight connection between two devices while transmitting current. These types of connectors typically require at least two poles to function, with one connected to the power supply and the other connected to the device that requires electricity.
Many types of twist-lock connectors are used in vehicle applications for jump-starting or connecting a towed vehicle. The process of connecting two poles using a twist-lock connector is quite simple: connect one end of an insulated wire (usually about twelve inches long) to each pole, then firmly grasp the exposed metal parts at each end and turn them counterclockwise until they appear locked together.
Pin and Socket Connectors
Pin and socket connectors consist of two separate parts: a male connector (sometimes referred to as a pin) and a female receptacle (or socket). The male connector inserts into the female receptacle to complete an electric circuit. There are some types of pin and socket connectors that have a locking mechanism to hold the connection in place, while others rely on the friction between each pole for stability.
In either case, these connectors require at least two poles to operate. Pin and socket connectors are most commonly used for connecting individual wires or components. In many cases, they can be connected in a daisy chain, which allows electrical current to flow through the series from one device to another.
Blade and Bayonet Connectors
Blade and bayonet connectors both have insulated blades that insert into receptacles to make a connection with an electric circuit. The difference between the two is how they lock into place once inserted: a bayonet connector features a rotating half-cylinder-shaped pin that forces the blade of the connector into place, while a blade connector inserts by sliding its flat metal prongs into locking grooves on either side of the receptacle.
Although these types of connectors may seem similar at first glance, they each have very different uses. For example, blade connectors are typically used for connecting individual wires or small components such as resistors and capacitors. Bayonet connectors on the other hand are used to terminate larger cables to make connections with power sources or electronic equipment using a special plug called an IEC 60320 C19 coupler.
D-Sub Connectors
D-sub connectors consist of two long metal pins on either end of a plastic insulator that serves to protect the circuit against electricity while allowing it to conduct current. These types of connectors are commonly used for terminating patch panels in computer networks, usually combining at least three circuits into one connection point via punch-down blocks on the back end of the patch panel.
This allows electricians to quickly distribute electricity to computers on a network with little effort, saving time and minimizing the need for extra wires. D-sub connectors are available in many different variations, including male, female, and even port connectors. D-sub connectors are sometimes referred to as D-subminiature connectors due to their small size (about one inch in height).
XLR Connectors
XLR connectors are commonly used for microphones on stage or in recording studios because they feature three cables that can be combined into one connection point while protecting electricity. The cable features a black rubber cover like other types of plugs do, but it is much larger than other cables because it fits both the male and female ends of the connector at once; each end has an outer metal shell with two poles inside.
A latch on each side secures the cables inside when they are not being used, making them very difficult to accidentally disconnect. XLR connectors can be used with either balanced or unbalanced circuits, depending on the type of connection desired.
Learning about connectors can be a confusing task, especially when they all serve the same general purpose of transferring electricity from one circuit to another.
There is a lot of overlap between the various types of connectors, and they all serve specific purposes that oftentimes depend on their size or shape. For this reason, it is crucial to understand how different types work and what unique properties they each offer to choose the right ones for your new project.










